Rapid Prototyping and Additive Manufacturing Technology
Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) data. Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or "additive layer manufacturing" technology.
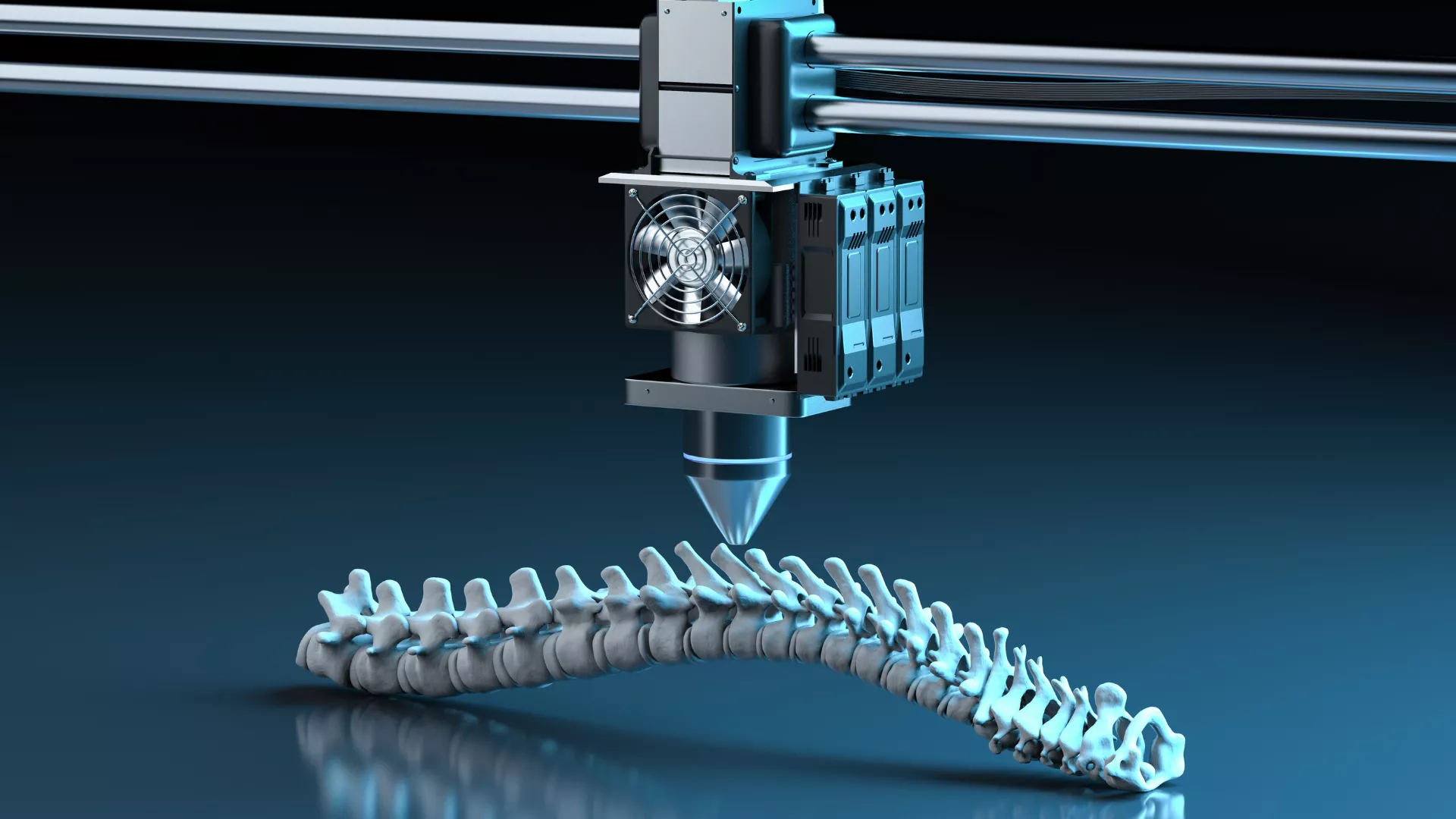
Rapid prototyping allows designers and engineers to create physical prototypes of their designs in a much shorter time than traditional manufacturing methods. This allows them to evaluate and iterate on their designs more quickly, which can lead to better products.
There are different rapid prototyping techniques available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Few of the most common rapid prototyping techniques include:
- Stereolithography (SLA): This technique uses a laser to cure a liquid resin layer by layer. The cured resin solidifies to form the object.
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM): This is the most common type of 3D printing. It uses a heated nozzle to melt thermoplastic filament, which is then deposited layer by layer to create the object.
- Selective laser sintering (SLS): This technique uses a laser to sinter powdered material layer by layer. The sintered powder particles fuse together to form the object.
WHAT WE COVERED IN THIS WEBINAR
At the end, we have covered the list of services we offer in this regard, which includes
This webinar was presented by Decos, a cutting-edge technology services partner ready to meet your software needs in the healthcare domain.
If you have any questions about this webinar or you seek advice on rapid prototyping on your medical device project, please contact Devesh at devesh.agarwal@decos.com. We would love to discuss it with you!
Discover more

Precision Medicine: Leveraging AI and Predictive Modelling for Personalized Healthcare

Concept to Care: Human Factors & AI in Medical Devices


