The Intersection of Human Factors and AI: Opportunities and Challenges
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries by driving automation, smarter decision-making, and next-level predictive capabilities. But to unlock AI's true potential, integrating AI with Human Factors Engineering (HFE) is key.
Human Factors Engineering (HFE) focuses on optimizing the interaction between humans and systems by considering human capabilities and limitations. This article explores the synergy between AI and human factors, highlighting real-world applications and actionable insights on how they can revolutionize user experiences, improve decision-making, and increase efficiency.
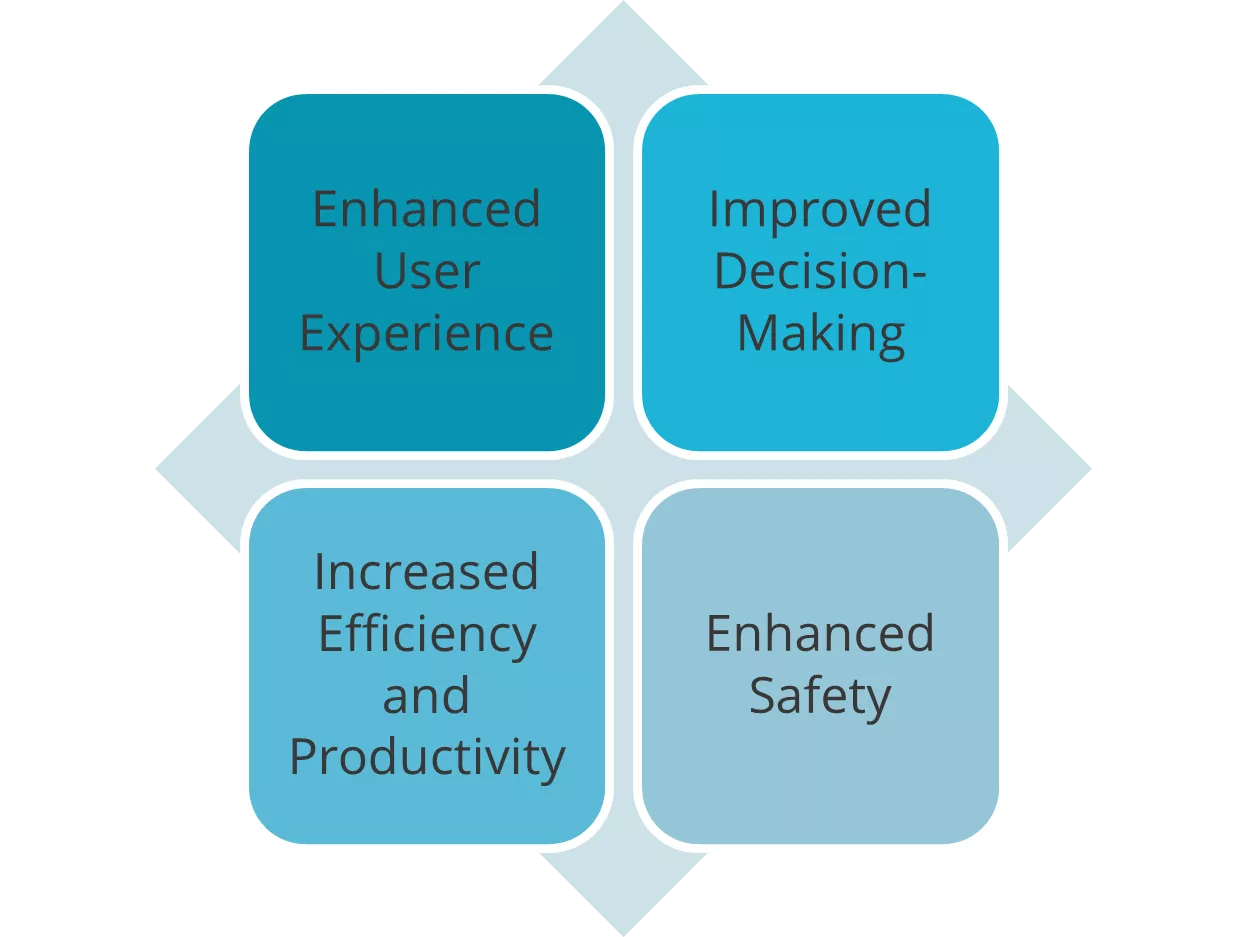
1. Enhanced User Experience
AI-driven personalization is revolutionizing user interactions by adapting to individual preferences and behaviours and delivering ultra-personalized experiences. By aligning AI with human factors, we can create systems that delight users, enhance engagement, and exceed expectations."When AI systems are designed with human factors principles in mind, they become more adept at anticipating user needs, minimizing cognitive load, and ensuring intuitive interactions. This synergy between AI and human factors leads to systems that not only meet but exceed user expectations.
Example: Voice-activated assistants such as Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant leverage AI to understand normal language and respond to user commands. By incorporating human factors principles, such as understanding natural language processing (NLP) nuances and considering user mental models, these systems enhance speech recognition accuracy and provide contextually relevant feedback. This integration ensures that the AI can handle diverse accents, speech patterns, and varying command structures, simplifying complex tasks and fostering a more seamless and enjoyable user experience. For instance, incorporating human-centred design principles allows these systems to adapt to user preferences over time, ensuring that responses become more tailored and relevant, reducing frustration and enhancing usability.
2. Improved Decision-Making
AI excels at processing large volumes of data and detecting patterns that might be overlooked by humans. By integrating human factors, AI systems can present this complex information in a way that supports and enhances human decision-making. This collaboration ensures that insights are not only accurate but also easily interpretable and actionable, facilitating more informed decisions.
Example: In healthcare, AI-powered diagnostic tools are transforming how doctors detect and diagnose diseases, offering faster, more accurate insights by analyzing patient data and medical images.. Integrating human factors principles involves designing interfaces that present diagnostic information in a clear and actionable format, For instance, incorporating visualization techniques such as color-coded indicators or annotated images can highlight critical areas, allowing doctors to quickly identify anomalies and make informed decisions. This approach not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also reduces the cognitive load on healthcare professionals, leading to more efficient and timely medical interventions.
3. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
AI can automate repetitive and mundane time-consuming tasks,allowing human workers to focus on more complex, higher-order and creative tasks. This article explores the synergy between AI and human factors, highlighting real-world applications and actionable insights on how they can revolutionize user experiences, improve decision-making, and increase efficiency. This involves designing interfaces and interaction points that align with human cognitive processes and work habits, thus minimizing errors and enhancing overall productivity.
Example: In manufacturing, AI-driven robots perform repetitive tasks like assembly line work, while human operators handle quality control and manage exceptions. By applying human factors principles to the design of control interfaces and workflow management systems, these systems can be optimized to match human cognitive capabilities. For instance, incorporating ergonomic principles into the design of robot control panels and alerts, can reduce mental strain on operators, streamline task transitions, and enable more effective supervision. This thoughtful design approach ensures that human workers can focus on complex problem-solving and creative tasks, ultimately boosting productivity and job satisfaction.
4. Enhanced Safety
AI systems can predict and prevent potential hazards, significantly enhancing safety across various environments. When designed with human factors in mind, these systems provide actionable and clear alerts, allowing users to act swiftly and confidently to avoid accidents.
Example: In aviation, AI analyzes flight data to anticipate maintenance needs and identify potential safety issues. By incorporating human factors principles, such as designing user-friendly dashboards and integrating alert systems into existing maintenance workflows, AI can present critical safety information in a clear and actionable format. For instance, AI systems can highlight potential issues with intuitive visual indicators and provide context-specific recommendations. This ensures that maintenance crews can quickly and accurately address issues before they escalate, enhancing overall flight safety and reliability.
1. Building Trust and Transparency
One of the key challenges in AI development is fostering user trust by ensuring that AI decisions are transparent. Users need to understand how AI systems operate and feel confident in their reliability. Achieving transparency in AI algorithms and ensuring that users can interpret AI outputs are are crucial for fostering confidence.
Solution: Incorporating explainable AI (XAI) techniques into the design of AI systems can significantly enhance transpsarency. XAI offers clarity on decision-making processes, enabling users to understand and trust the system’s outputs. Additionally, employing clear communication strategies and visualization of AI processes can further demystify how decisions are made, reinforcing user confidence and trust in the system.

2. Human-AI Collaboration
Effective collaboration between humans and AI requires careful clear task division and how information is shared. Misalignment in how tasks are allocated or how information is exchanged can lead to confusion, errors, and inefficiencies.
Solution: Defining clear roles for both humans and AI can help users collaborate efficiently with AI systems. This includes defining specific roles, responsibilities, and workflows that leverage the strengths of both human and AI capabilities. Providing regular training and updates ensures that users remain proficient in making use of the AI systems and adapting to the evolving collaborative processes.
3. Addressing Ethical and Bias Concerns
AI systems can unintentionally perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or unethical outcomes. Tackling these biases and ensuring the ethical use of AI presents a significant challenge.
Solution: Implementing rigorous testing and validation processes to identify and mitigate biases is crucial. Incorporating diverse datasets and involving multidisciplinary teams in AI development process contribute to create more equitable and fair AI systems. Establishing ethical guidelines and oversight mechanisms ensures that AI is used responsibly and fairly, minimizing potential biases and promoting ethical practices.
4. Ensuring User Training and Adaptation
With the increasing prevalence of AI systems, ensuring that users are well-trained and able to adapt to new technologies poses a challenge. Without adequate training, users may struggle to effectively use AI systems, potentially diminishing their benefits.
Solution: Developing comprehensive training programs that cover both the technical and practical aspects of AI systems is crucial. Providing continuous support and resources help users adapt to the changes and stay updated with new features and capabilities, ensuring they remain adept at leveraging AI technologies effectively and fully realizing their potential.
Conclusion
A Future Where AI and Human Factors Shape Innovation
The intersection of human factors and artificial intelligence (AI) opens up exciting opportunities to create systems that are not only powerful and intelligent but also user-friendly, intuitive, and ethical. By integrating human-centered design principles, we can craft AI solutions that enhance user experiences, improve decision-making, and drive efficiency.
However, these benefits come with their own set of challenges, including building trust, facilitating human-AI collaboration, addressing ethical concerns, and ensuring user adaptation. By focusing on human factors engineering, we can overcome these challenges and ensure that AI systems are not only advanced but also harmonious with human needs, providing benefits that are both practical and ethical.
The ongoing dialogue and partnership between these fields will be pivotal in shaping AI solutions that are not only effective but also enrich the human experience in a balanced and ethical manner.
How can Decos help you?
Leveraging our expertise in human factors engineering, we ensure that systems and processes are designed with a deep understanding of human capabilities and needs. We provide specialized solutions to enhance usability and effectiveness, including user-centered design and tailored training to align implementations with your team’s operational requirements.

This blogpost is written by Deepareddy G, Sr. Systems Engineer (Human Factors) at Decos. She is an expert in Systems, Human Factors, RA&QA and comes with wealth of experience in medical device regulations, R&D, Usability/ Human Factors.
Decos is a cutting-edge technology services partner ready to meet your diverse needs across various industries, including the medical domain. If you have a question about one of our projects or would like advice on your project or a POC, contact Devesh Agarwal. We’d love to get in touch with you!
References:
- Ahmed Al Kuwaiti, Khalid Nazer, Abdullah Al-Reedy, Shaher Al-Shehri, Afnan Al-Muhanna, Arun Vijay Subbarayalu, Dhoha Al Muhanna and Fahad A. Al-Muhanna, “A Review of the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare”.
- Sebastian Voigtlaender, Johannes Pawelczyk, Mario Geiger, Eugene J. Vaios, Philipp Karschnia, Merit Cudkowicz, Jorg Dietrich, Ira R. J. Hebold Haraldsen, Valery Feigin, Mayowa Owolabi, Tara L. White, Paweł Świeboda, Nita Farahany, Vivek Natarajan & Sebastian F. Winter. Neurology Journal, 2023, “Artificial Intelligence in Neurology: Opportunities and Challenges”.
- Gebreyes, K., Wainstein, J., Gerhardt, W., & Korenda, L, “Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Foundations, Opportunities, and Challenges”.
- Parasuraman, R., & Miller, C. A. (2020), “Automation, Decision Making, and Human Performance: Emerging Challenges and Opportunities”.
- Atul Raj (Aug 2023), “Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A review”
- Fei Jiang, Yong Jiang, Hui Zhi, Yi Dong, Hao Li, Sufeng Ma, Yilong Wang, Qiang Dong, Haipeng Shen, Yongjun Wan, “Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future”.
Discover more
Exploring Degrees of Freedom: From Mechanics to Robotics

Design for Disassembly: A Path to Sustainable Product Lifecycles

